A meteoroid is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space. Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than this are classified as micrometeoroids or space dust. Most are fragments from comets or asteroids, whereas others are collision impact debris ejected from bodies such as the Moon or Mars.
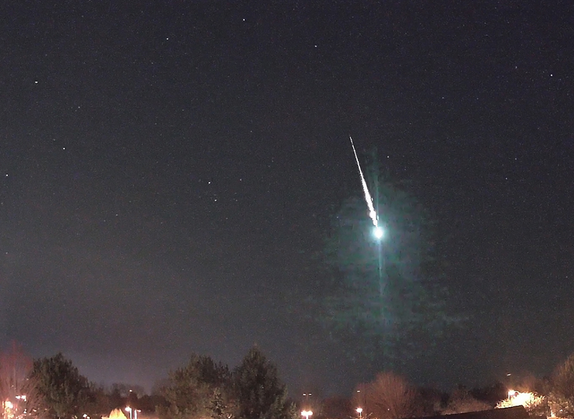
When a meteoroid, comet, or asteroid enters Earth’s atmosphere at a speed typically in excess of 20 km/s (72,000 km/h; 45,000 mph), aerodynamic heating of that object produces a streak of light, both from the glowing object and the trail of glowing particles that it leaves in its wake. This phenomenon is called a meteor or “shooting star”.
Meteors typically become visible when they are about 100 km above sea level. A series of many meteors appearing seconds or minutes apart and appearing to originate from the same fixed point in the sky is called a meteor shower.
A meteorite is the remains of a meteoroid that has survived the ablation of its surface material during its passage through the atmosphere as a meteor and has impacted the ground.